Comparative anatomy of venom glands suggests a role of maternal secretions in gall induction by cynipid wasps (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae)
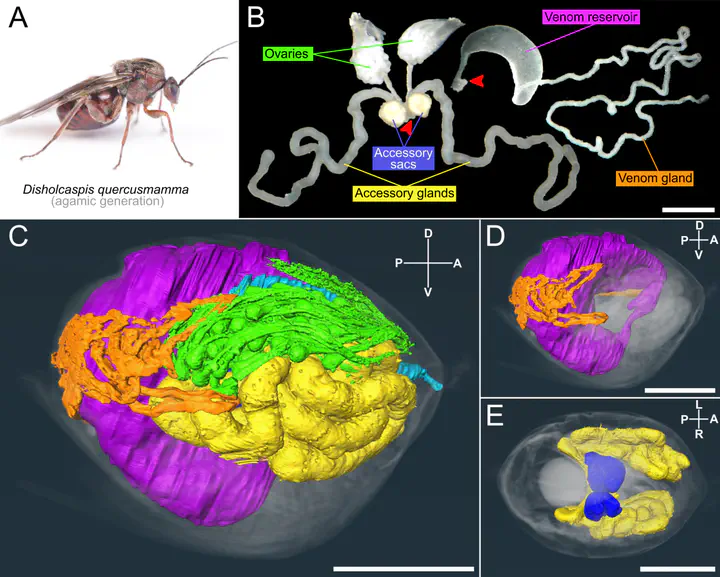 Image credit: [Antoine Guiguet]
Image credit: [Antoine Guiguet]Abstract
Many herbivorous insect species are capable of hijacking plant development to induce novel plant organs called galls. In most groups of galling insects, the insect organs and molecular signals involved in gall induction are poorly understood. We focused on gall wasps (Hymenoptera:Cynipidae), the second largest clade of gall inducers (~1,400 spp.), for which the developmental stages and organs responsible for gall development are unclear. We investigated the female metasomal anatomy of 69 gall-inducing and 29 non-gall-inducing species across each of the major lineages of Cynipoidea, to test relationships between this lifestyle and the relative size of secretory organs. We confirmed that the venom apparatus in gall-inducing species is greatly expanded, although gall-inducing lineages vary in the relative size of these glands. Among these gallers, we measured the largest venom gland apparatus relative to body size ever recorded in insects. Non-galling inquiline species are accompanied by a reduction of this apparatus. Comparative microscopic analysis of venom glands suggests varying venom gland content across the lineages. Some oak gallers also had enlarged accessory glands, a lipid-rich organ whose function remains unclear, and which has not been previously studied in relation to gall formation. Together, the massive expansion of secretory organs specifically in gall-inducing species suggests a role of these secretions in the process of gall formation, and the variance in size of venom glands, accessory glands, and the contents of these glands among gallers, suggests that gall formation across this clade is likely to employ a diversity of molecular strategies.